Yes, moldy corn can sometimes be used to produce animal feed, but only under strict conditions and after proper detoxification and safety assessment.
Richi machinery is a very professional feed machinery manufacturers, you can customize a full set of feed production line solutions. Of course, we know a lot about feed machinery.But our major is also based on a premise: we know the feed, including feed raw materials, animal breeding, feed formula and other aspects. Because only in this way, we can design, manufacture truly meet the feed mill, farmers demand for feed production equipment. Today, for the special raw materials - moldy corn, ruiqi machinery to provide you with some professional processing methods:
When Can Moldy Corn Be Used in Animal Feed?
- Mild Mold Contamination Only:
- If the corn shows minor mold growth but has not produced significant levels of mycotoxins (like aflatoxins, DON, zearalenone), it might be salvageable after cleaning and testing.
- After Proper Processing:
- Mechanical cleaning: Removing visibly moldy or discolored kernels.
- Drying: Reduces further mold development.
- Detoxification methods:
- Physical: Heat treatment, ammoniation (in some regions).
- Chemical: Use of binders like bentonite or activated carbon in feed.
- Biological: Enzyme or microbial detoxification (still developing technology).
- Strict Mycotoxin Testing Is Required:
- Feed mills must test for mycotoxin levels (especially aflatoxin, fumonisin, zearalenone, and DON).
- If levels exceed legal limits, the corn must not be used for feed.
When Should Moldy Corn NOT Be Used?
- If the mold is extensive or visibly dark/black, it likely contains dangerous levels of mycotoxins.
- If toxins exceed legal thresholds, it can cause:
- Liver/kidney damage
- Reproductive issues
- Death in severe cases (especially in pigs and poultry)
Species Sensitivity to Mycotoxins
| Animal | Sensitivity | Common Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Pigs | Very High | Vomiting, immune suppression |
| Poultry | High | Liver damage, poor growth |
| Ruminants | Moderate | Some detoxification in rumen, but still at risk |
| Fish | Very High | Reduced feed intake, organ damage |
Best Practices for Using Moldy Corn in Animal Feed Production
- Always test for mycotoxins before use.
- Avoid mixing moldy corn with clean corn to “dilute” toxins — this is often illegal and unethical.
- Consult a veterinary nutritionist or feed safety expert.
- Document all steps taken for traceability and quality control.
Feed Mill Equipment Tips for Handling Moldy Corn
When processing moldy corn for animal feed production, it is essential to reduce the risk of contamination, ensure animal safety and comply with feed safety regulations. This requires a combination of specialized equipment, monitoring systems and process controls in the feed plant. RICHI Machinery has been designing, manufacturing and exporting animal feed mill equipment for more than 30 years, and with the experience of a large number of customers, we are able to re-design a complete animal feed production line and equipment configuration taking into account the raw material, the size of the site, and even the budget of the customer. The following is the equipment configuration we suggest for processing moldy corn for animal feed production: 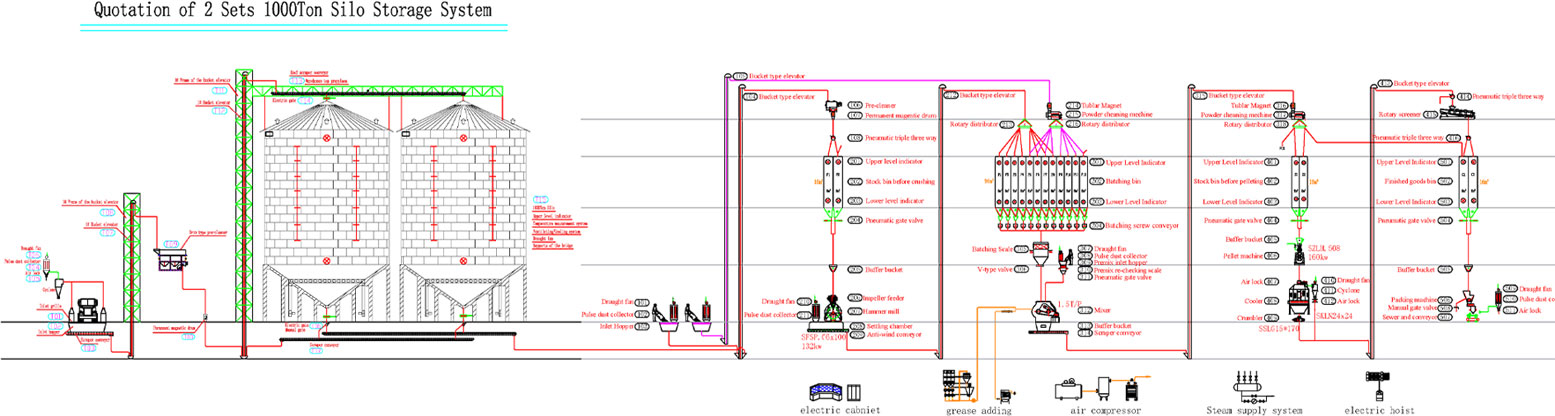
- Raw Material Receiving and Initial Cleaning
- Objective: Eliminate impurities and segregate unacceptable raw materials.
- Key Equipment:
- Receiving Hopper with Pre-Cleaner: Removes large debris, husks, and visibly moldy grains.
- Magnetic Separator: Captures metal contaminants to protect downstream equipment.
- De-stoner: Eliminates heavy particles like stones.
When moldy corn is used, this stage helps reduce fungal load by removing visibly spoiled kernels.
- Drying and Moisture Control
- Objective: Ensure optimal moisture content (< 14%) for storage and further processing.
- Key Equipment:
- Grain Dryer: Reduces moisture in corn to inhibit mold growth.
- Moisture Sensors: Continuously monitor moisture levels in real time.
Drying is critical to preventing further mycotoxin formation from residual mold.
- Mycotoxin Monitoring and Detoxification (When Using Moldy Corn)
- Objective: Detect and neutralize harmful mycotoxins.
- Key Equipment:
- Mycotoxin Testing Lab (Rapid Kits / ELISA / HPLC): Detect levels of aflatoxin, DON, zearalenone, etc.
- Mycotoxin Binder Dosing System: Automatically adds toxin binders (e.g. bentonite, zeolite) during batching.
This is a safety-critical step when using any questionable or contaminated material.
- Dosing and Batching
- Objective: Accurately weigh and proportion ingredients according to feed formula.
- Key Equipment:
- Automatic Batching System: Doses materials based on premixed recipes.
- Silo and Hopper Systems: Store various raw materials like corn, soybean meal, DDGS, vitamins, etc.
Ensures each feed batch maintains consistency in nutrients and detoxification additives.
- Grinding
- Objective: Reduce particle size to improve digestibility and pellet quality.
- Key Equipment:
- Hammer Mill or Grinder: Processes corn and other grains to a fine, uniform size.
- Air Separator / Dust Collector: Controls fine dust and improves cleanliness.
Finer grinding is especially important for young animals and poultry.
- Mixing
- Objective: Homogenize all ingredients and additives.
- Key Equipment:
- Double Shaft Paddle Mixer / Ribbon Mixer: Blends all components uniformly.
- Liquid Additive System (optional): Adds oils, molasses, or enzyme solutions.
A uniform mix ensures each pellet delivers the full nutritional and safety profile.
- Pelletizing
- Objective: Compress feed into dense, uniform pellets.
- Key Equipment:
- Feed Pellet Mill (Ring Die):
- Common pellet sizes: 2–12mm
- Adjustable for different animal species
- Conditioner (Pre-pelletizer): Injects steam or heat to improve pellet durability.
High temperature helps destroy remaining pathogens and stabilize the product.
- Feed Pellet Mill (Ring Die):
- Cooling
- Objective: Reduce pellet temperature and moisture post-pelletizing.
- Key Equipment:
- Counterflow Cooler: Cools pellets uniformly to room temperature.
- Cyclone Dust Collector: Removes moisture-laden air and dust.
Essential to prevent mold reformation and improve shelf life.
- Screening and Crumbling (if needed)
- Objective: Remove fines and adjust pellet size for small animals.
- Key Equipment:
Fines can be recycled back to the mixer or pellet mill.
- Packaging and Storage
- Objective: Bag, label, and store finished feed safely.
- Key Equipment:
- Automatic Bagging Machine: Fills and seals 20–50 kg bags.
- Sewing / Heat Sealing Machine
- Palletizing & Wrapping Unit
- Warehouse with Temperature & Humidity Control
Proper storage is crucial when moldy raw materials were used, to avoid secondary contamination.
Animal Feed Mill Equipment Flowchart Overview
| Process Stage | Equipment Highlights |
|---|---|
| Cleaning & Separation | Pre-cleaner, magnetic separator, de-stoner |
| Drying | Grain dryer, moisture meter |
| Toxin Control | Mycotoxin testing kit, binder dosing system |
| Grinding | Hammer mill, air separator |
| Batching & Mixing | Automatic batching scale, mixer, additive system |
| Pelletizing | Pellet mill, conditioner |
| Cooling & Screening | Cooler, screener, crumbler |
| Packaging & Storage | Bagging machine, sewing machine, palletizer |
Reminders on the use and production of moldy corn from RICHI Machinery
Even if advanced production and processing equipment and animal feed pellet production technology are used, moldy corn can only be used under the following circumstances:
- It passes mycotoxin testing,
- It's processed with binders and strict control,
- Animal species-specific sensitivity is considered.


