Feed Usage Problems and Solutions for Small Layer Hen Farms
At present, farm-scale chicken farming has changed from a subsidiary industry to an important pillar industry of the family economy. Generally, about 1,000 layer hens are raised, and the total investment is not too large. It does not affect the management of farmland, nor does it need to hire people to help, and it can also create considerable profits for the family. This is the rapid development of small layer hen farms in recent years. However, due to the low technical level of such chicken farms, there are many problems in production, especially in the use of feed. Today, Richi Machinery will explain the main problems and solutions in the use of feed in small chicken farms.

1. What Kind of Feed is Suitable for Laying Hens?
- Powder feed: Obtained by grinding raw materials and adding vitamins, trace elements, etc. Advantages: complete nutrition, chickens less likely to pick feed; Disadvantages: poor palatability, easy to cause waste if too fine.
- Pellet feed: Pelleted feed (2.5–5.0 mm diameter) prepared from powder. Advantages: balanced nutrition, prevents selective eating, supports mechanized feeding; Disadvantages: higher processing cost, may cause over-fat hens, affecting egg production. Recommended in hot summer to stimulate intake.
Common feeding methods:
- Dry powder feeding: Free access with feeders, minimal nutrition gap, labor-saving.
- Wet mix feeding: Feed mixed with water several times a day; better palatability but weaker chickens may not get enough nutrients.
2. How to Process Layer Feed for Laying Hens
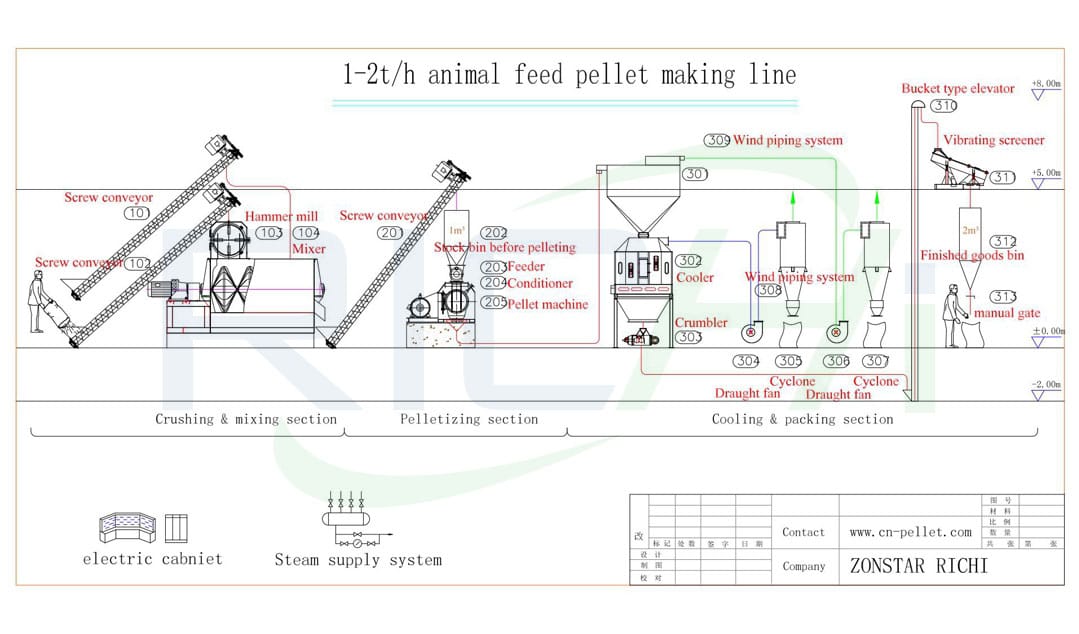
- Mash feed process: Cleaning → Crushing → Mixing → Packing. Main equipment: chicken feed hammer mill grinder, chicken feed mixer, bagging machine, screener.
- Pellet feed process: Cleaning → Crushing → Mixing → Pelleting → Cooling → Packing. Main equipment: chicken feed hammer mill grinder, chicken feed mixer, poultry chicken feed pellet mill, chicken pellet cooler, packing machine.
3. Common Problems in Chicken Feed Preparation
- Excessive energy: Too much corn leads to ovarian fat and reduced egg production.
- Excessive crude protein: Overuse of soybean meal, peanut meal, fish meal increases costs and may cause toxicity.
- Calcium–phosphorus imbalance: Low calcium levels (<1%) during peak laying cause thin or soft-shelled eggs. Ideal: 3.5–3.7% Ca and 0.45% P.
- Blind vitamin/mineral addition: Incorrect dosages or over-reliance on green feed leads to nutrient imbalances.
- Single feed formula: No adjustments for breed, age, or production stage reduces performance.
- Improper drug addition: Self-prescribed medications cause poisoning, poor growth, and low productivity.
4. Solutions

- Organize chicken raising knowledge and adjust feed formula according to breed and stage.
- Apply protein and energy scientifically to meet needs and reduce waste.
- Use minerals accurately (e.g., 3.6% Ca, 0.45% P for laying hens).
- Regulate vitamin use—supplement with compound vitamins instead of relying solely on green feed.
- Design feed formulas according to breed, stage, flock condition, feed availability, market, and season.
5. Recommended Feed Formulas for Laying Hens

| Stage | Ingredients & Percentage |
|---|---|
| 1–3 weeks | Corn 60%, Millet 5%, Sorghum 4%, Wheat bran 5%, Bean cake 8%, Fish meal 8%, Bone meal 3%, Blood meal 5%, Stone meal 1.5%, Salt 0.3%, Additives as needed. |
| 4–6 weeks | Corn 60%, Sorghum 4%, Wheat bran 6%, Bean cake 15%, Peanut cake 3%, Cotton cake 2%, Blood meal 3%, Fish meal 5%, Shell meal 1%, Bone meal 0.7%, Salt 0.3%. |
| 7–14 weeks | Corn 60%, Sorghum 6%, Barley 12%, Bean cake 10%, Fish meal 3%, Shell meal 0.7%, Locust leaf meal 5%, Bone meal 2%, Salt 0.3%, Additives as needed. |
| 15–25 weeks | Corn 65%, Barley 5%, Wheat bran 15%, Bean cake 7%, Cotton cake 2%, Fish meal 2%, Shell meal 1.5%, Bone meal 2%, Salt 0.3%, Additives as needed. |
| 50% egg production | Corn 60%, Wheat bran 6%, Sweet potato 6%, Bean cake 18%, Fish meal 6%, Bone meal 2.7%, Salt 0.3%, Methionine 0.1%, Additives as needed. |
| 55–80% egg production | Corn 57%, Dried sweet potato 5%, Wheat bran 3%, Bean cake 20%, Cotton cake 2%, Peanut cake 2%, Fish meal 7%, Bone meal 3%, Salt 0.3%, Additives as needed. |
| Above 80% egg production | Corn 52%, Sorghum 4%, Wheat bran 4%, Bean cake 20%, Cotton cake 4%, Peanut cake 4%, Fish meal 4%, Locust leaf meal 3.5%, Bone meal 3.5%, Salt 0.3%, Additives as needed. |


